Downloading ML training reports
You can download training reports for models you train in an experiment. The training report includes comprehensive details about the processes that trained a model, and optionally other models in the ML experiment. You can download training reports from ML experiments and ML deployments to which you have access. Training reports are in PDF format.
Admins can also download training reports from the Administration activity center. For more information, see Downloading ML training reports as an administrator.
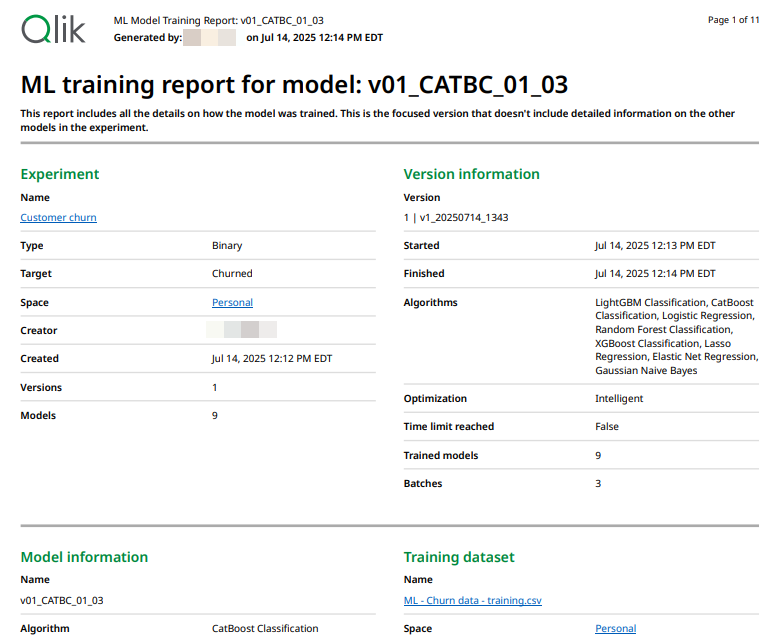
ML training report
Use cases
With model training reports, you can:
-
Dive deeper into the processes that train your models—for example, for auditing purposes.
-
Easily share details about model training with users outside of Qlik Cloud.
Generating a training report
From an experiment
Do the following:
-
Open an ML experiment.
-
Go to the Models tab.
-
Select a model.
-
In the top right corner, click Download training report.
-
In the dialog, optionally on Include information about all models in the experiment.
When activated, this setting generated an expanded report containing information about all models trained in the experiment.
-
If needed, click Preview to view the report without downloading it. Depending on your browser, you might need to attempt this more than once.
-
Click Download. The report generates and is saved to your local Downloads folder.
You can also generate a training report by clicking on a model, and selecting Download training report.
From an ML deployment
Do the following:
-
Open an ML deployment.
-
Go to the Deployable models tab.
-
Under All models in the deployment, click
next to a model.
-
Select Download training report.
-
In the dialog, optionally on Include information about all models in the experiment.
When activated, this setting generated an expanded report containing information about all models trained in the experiment. See Full and focused versions.
-
If needed, click Preview to view the report without downloading it. Depending on your browser, you might need to attempt this more than once.
-
Click Download. The report generates and is saved to your local Downloads folder.
As an administrator
Administrators can also download training reports from the Administration activity center. For more information, see Downloading ML training reports as an administrator.
What is included in a training report
The training report outlines, in detail, the following information. Some details might only be present if you download the full version of the training report. For more information, see Full and focused versions.
-
Who created the experiment
-
When experiments and model were trained
-
Location and name of resources used in training
-
How many versions and models the experiment has
-
The algorithms used to train models
-
Details about the training datasets used, such as how much data they contain
-
Processing that was performed on training data before and during training
-
Model metrics for both training and holdout data
-
Hyperparameter data
Full and focused versions
When downloading a training report, the user can optionally turn on a setting named Include information about all models in the experiment. This setting controls whether the full or focused version of the report is generated.
With the Include information about all models in the experiment setting turned on, the full version of the report is generated. This report contains additional information about other models trained in the experiment.
On the other hand, the focused report only contains information about the selected model. Information about other models in the experiment is not included.
Interpreting terms in the training report
When analyzing training reports, it is assumed that you have an understanding of the technical terms referenced. Most terms are explained in the Qlik Predict help documentation.
The following table provides definitions for content in the report, along with useful help topics.
| Term | Meaning | Associated content |
|---|---|---|
| Batches |
Refers to how many batches of models were trained in the experiment. When using intelligent model optimization, models are trained in iterative batches to improve training performance and results. By contrast, an experiment version that does not use intelligent model optimization — that is, manual optimization — trains models in a single batch. |
- |
| EDA | Refers to exploratory data analysis. This is a term for an automatic set of processing that is performed on training data before model training begins. | Experiment setup |
| Encoding, Impact encoded, One-hot encoding | Refers to processing applied to feature data to make it more usable in model training. | Categorical encoding |
| Feature engineering | Refers to numerous processes that result in new features. These can be new features that are exposed as brand new entities, and also features that are created through encoding and free text processing. | |
| Five-fold cross-validation | Refers to the cross-validation that is performed on models after each iteration of training. | Holdout data and cross-validation |
| Optimization | Refers to whether model training used intelligent or manual optimization. | Working with model optimization |
| Sampling ratio | Refers to how much of the training dataset was used to train the model. When using intelligent model optimization, models can sometimes be trained on less than 100% of the original dataset, notably for very large datasets. By contrast, an experiment version that does not use intelligent model optimization — that is, manual optimization — always uses 100% of the training dataset. |
Sampling of training data |
| Split | Refers to an automatic splitting of the training dataset into training and holdout data. The holdout is not used for model training, but instead for testing model performance. | Holdout data and cross-validation |
| U=User override | Refers to the user action of manually changing the feature type from the automatically identified feature type. | Changing feature types |
Permissions
Permissions for downloading from an ML experiment
To export a training report from an ML experiment, you need view access to the experiment. In other words, you must meet the following requirements:
-
Professional or Full User entitlement in the Qlik Cloudtenant.
-
One of the following:
-
Automl Experiment Contributor built-in security role
-
Automl Deployment Contributor built-in security role
-
Manage ML experiments permission set to Allowed via User Default or custom security role
-
Manage ML deployments permission set to Allowed via User Default or custom security role
-
Manage ML experiments and deployments admin permission set to Allowed via custom security role
-
-
For experiments in shared spaces, one of the following space roles in the space:
-
Owner (of the space)
-
Can manage
-
Can edit
-
Can view
-
Permissions for downloading from an ML deployment
To export a training report from an ML deployment, you need view access to both the deployment and the experiment from which it was deployed.
In other words, you must meet the following requirements:
-
Professional or Full User entitlement in the Qlik Cloudtenant.
-
One of the following:
-
Automl Experiment Contributor built-in security role
-
Automl Deployment Contributor built-in security role
-
Manage ML experiments permission set to Allowed via User Default or custom security role
-
Manage ML deployments permission set to Allowed via User Default or custom security role
-
Manage ML experiments and deployments admin permission set to Allowed via custom security role
-
-
For experiments in shared spaces, one of the following space roles in the space:
-
Owner (of the space)
-
Can manage
-
Can edit
-
Can view
-
-
For deployments in shared spaces, one of the following space roles in the space:
-
Owner (of the space)
-
Can manage
-
Can edit
-
Can view
-
-
For deployments in managed spaces, one of the following space roles in the space:
-
Owner (of the space)
-
Can manage
-
Can contribute
-
Can view
-
Limitations
-
Training reports are only available for ML experiments created in late July 2025 and later.
