Join processor
Combines two flows based on one or more keys.
The Join processor allows you to combine data from two output flows. Choose a common key, select the type of join, and combine the data in the output flow.
Usage
The Join processor requires two input flows and can generate only one output flow.
Properties
Properties to configure in order to combine your records using Join.
| Property | Configuration |
|---|---|
| Join type |
Select the desired join type in the list:
|
| Conditions |
|
To rename the processor or edit its description, point your mouse over the name or description to change in the Properties panel and click the Edit icon.
Additional information about join operations
The Join processor allows you to apply four different types of join operations to your data.
Inner join
This type of join operation is used to:
-
match the values that are common between two datasets.
-
create a result set with all the pairs that match.
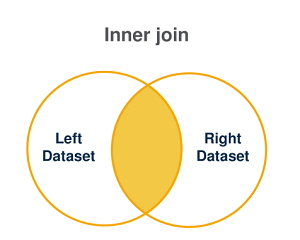
The result set is determined as follows:
| If the join statement is satisfied (dataset L matches dataset R) | If the join statement is not satisfied |
|---|---|
| All matching records are combined and returned in the result set. | Non-matching records are ignored. |
Left outer join
This type of join operation is used to:
-
match the values that are common between two datasets AND retain all the values that exists in the left dataset.
-
create a result set combining these records.
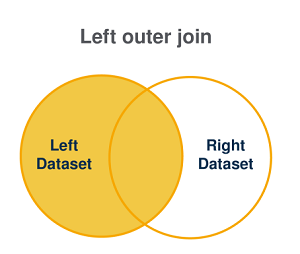
The result set is determined as follows:
| If the join statement is satisfied (everything that is in dataset L + matches in the two datasets) | If the join statement is not satisfied |
|---|---|
| All records in the left dataset as well as the matching records between dataset left and dataset right are combined and returned in the result set. | Non-matching records are ignored. |
Right outer join
This type of join operation is used to:
-
match the values that are common between two datasets AND retain all the values that exists in the right dataset.
-
create a result set combining these records.
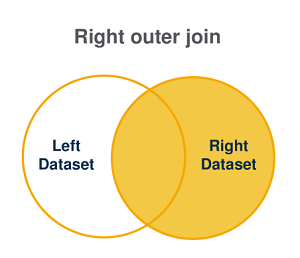
The result set is determined as follows:
| If the join statement is satisfied (everything that is in dataset L and R + matches in the two datasets) | If the join statement is not satisfied |
|---|---|
| All records in the left dataset as well as the matching records between dataset left and dataset right are combined and returned in the result set. | Non-matching records are ignored. |
Full outer join
This type of join operation is used to:
-
retain all the values that match in the left and right datasets.
-
create a result set combining these records.
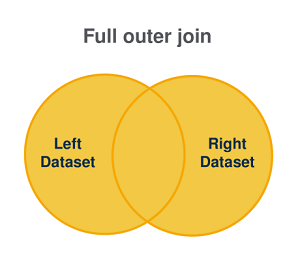
The result set is determined as follows:
| If the join statement is satisfied (everything that is in dataset L + matches in the two datasets) | If the join statement is not satisfied |
|---|---|
| All records in the left dataset as well as the matching records between dataset left and dataset right are combined and returned in the result set. | Non-matching records will be listed in the result set as NULL. |
