Running scripts
Run your load script to export data with the latest data from the data source.
Scripts in Qlik Cloud Analytics do not run automatically to update their outputs. Running the script runs the load script again to load the latest data from the script's data source and then exports it. Script runs can be manual or scheduled.
For information about which users can reload data, see:
You can check the run status of a script. This can be Success, Reloading, or Failed.
- In list view of scripts by clicking the value in the Last modified column.
- In Reload history.
- In the Schedule dialog for tasks configured for scheduled reloads of the script (only shows statuses for runs initiated by tasks).
Scheduling script runs
Create tasks to schedule runs of your script. The schedule can use time-based or event-based triggers.
To create a task:
-
Do one of the following:
-
In your activity center, click
on the script and select Schedule.
-
In your script, open the Overview section and click
> Schedule.
-
-
Click Create new task.
-
For Task name, enter a name for the task.
-
Optionally add a Description.
-
Under Based on, select the trigger for the task. You have the following options:
-
Time-based: Schedule the refresh to occur at a specific point in time. Then, configure the task with the associated settings for that trigger. For details, see Time-based schedules.
The following time-based triggers are available:
-
Daily
-
Weekly
-
Monthly
-
Yearly
-
-
Event-based: Schedule the refresh to start when a specific event takes place. For details, see Event-based schedules.
The following event-based triggers are available:
-
Another task succeeded
-
Another task failed
Information noteUse event-based triggers to create task chains for refreshing data. For further instructions, see Creating task chains for data refreshes. -
-
Time-based schedules
When you create a time-based schedule, you can choose:
-
The frequency and interval of the refresh
-
The timezone and time of day
-
How long the schedule will be in effect
Repeating refreshes can be set at the following intervals:
-
Daily: Set the times per day, timezone, and the time of day.
-
Weekly: Set the days of the week, times per day, timezone, and time of day.
-
Monthly: Set the days of the month, times per day, timezone, and time of day.
-
Yearly: Set the months, days of the month, times per day, timezone, and time of day.
For schedules running multiple times per day at any interval, you can also define the hours of the day within which the schedule runs. Specify a specific time for the schedule to start that day.
By default, schedules will run continuously, with no end date. You can choose to set a start date, an end date, or to only run the schedule between two dates.
Event-based schedules
Event-based schedules allow you to chain together tasks for different apps, scripts, data flows, and table recipes. This is useful for sequential refreshes of these assets.
For more information, see Creating task chains for data refreshes.
Managing tasks
You can manage existing tasks if you have the permissions to do so.
To view and manage tasks:
-
Do one of the following:
-
In your activity center, click
on the script and select Run > Schedule.
-
In your script, open the Overview section and click
> Schedule.
-
-
Click
next to a task, and select any of the available options. Alternatively, switch to the History tab to view a detailed history for when the task was executed.
For more information, see Managing tasks for data refreshes.
Limitations and considerations
-
A task for refreshing data is deactivated if it fails to execute five times in a row. If you own the task, you will receive notifications when this happens. Notification settings can be customized for a single app, all apps in a space, or all apps in a tenant. For more information, see Ownership of tasks.
-
If the task owner leaves or is deleted from the tenant, another user has to take ownership of the task, or delete and recreate it. Otherwise, its scheduled refreshes will fail. For information about how to change this ownership, see Ownership of tasks.
-
If you have a high number of queued and executing data refresh processes (and additional concurrent CPU and memory intensive processes), you might notice that some refresh processes execute, in some cases, noticeably after their scheduled start time.
-
Tasks for refreshing data are not included for the published copy of a script. Published scripts must have their tasks reconfigured on the version in the managed space.
-
If your script has tasks for refreshing data, and you move it between spaces (personal or shared spaces), these tasks are deactivated. You can reactivate them when ready to resume the scheduled refreshes. See Activating and deactivating a task.
Ownership of tasks
A task for data refreshes runs on behalf of the user who owns the task rather than the owner of the app, script, data flow, or table recipe. For the task to run successfully, the task owner must still have the correct access to the app, script, data flow, or table recipe and its data sources. Certain actions result in changes to who owns the task. The task owner is determined by the following rules:
-
When you create a task for running a script, you become the owner of that task.
-
If another user edits or saves an existing task, they become the new owner of that task.
-
If another user modifies the load script of the script, they become the new owner of all tasks for scheduled runs of that script.
For more information about co-developing script data models, see Collaboratively developing data load scripts in shared spaces.
Administering tasks for refreshing data
Tenant admins and analytics admins can edit and delete tasks for scheduled data refreshes. This is done in the Administration activity center. For more information, see:
Manually running scripts
You can run a script manually.
Do the following:
- Click
on the script and select Run now.
Viewing run history for a script
Reload history contains the run history for the selected script. Use it to help troubleshoot scheduled run issues. You can view the status, start and end times, and duration of past and current runs of the script. You can also view and download a corresponding log file.
There are two ways to view the reload history for a script.
- In Overview of a script, click Reload history.
- In the list view of scripts in the Analytics activity center, click the date in the Last modified column and select View reload history.
Reload history of a script
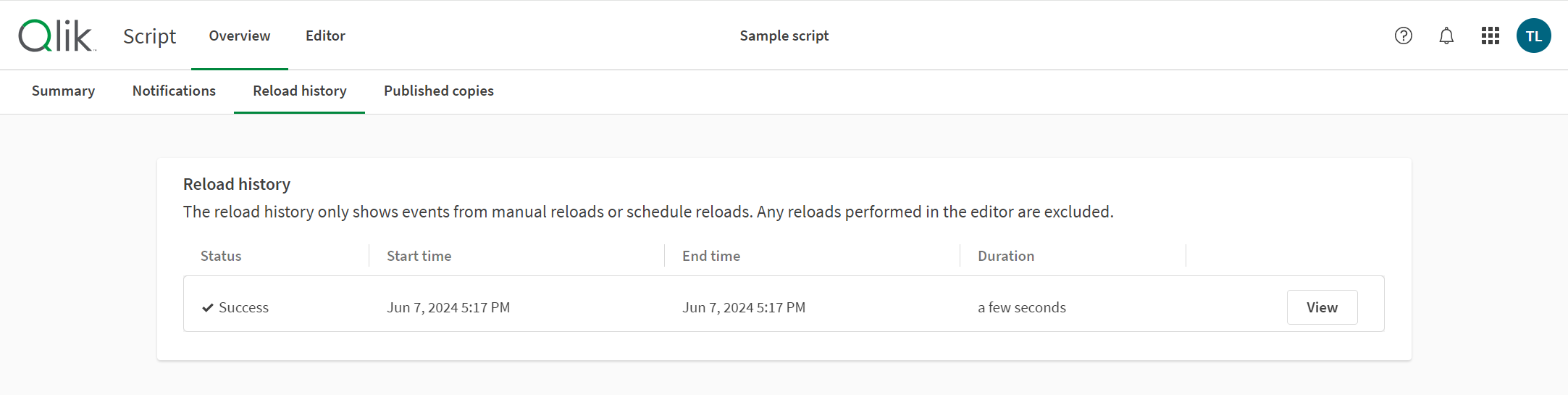
On the Reload history page, click the View button to view the run summary. Optionally, you can also download a detailed log file. When the limit for the number of logs stored is reached, new logs will replace the oldest logs, on a first in, first out basis.
You might want to cancel a run of your script if it is taking too long or the script has been updated with new data and you want to start a new run. To cancel a run, go to Reload history, and click Cancel.
You can see the canceled run in your Reload history.
Viewing history for tasks
In addition to the Reload history view, you can also view an execution history focused on the tasks created for scheduled reloads of the script. For more information, see Viewing the refresh history of a task.
Understanding timestamps: Updated, Modified date, and Last reload date
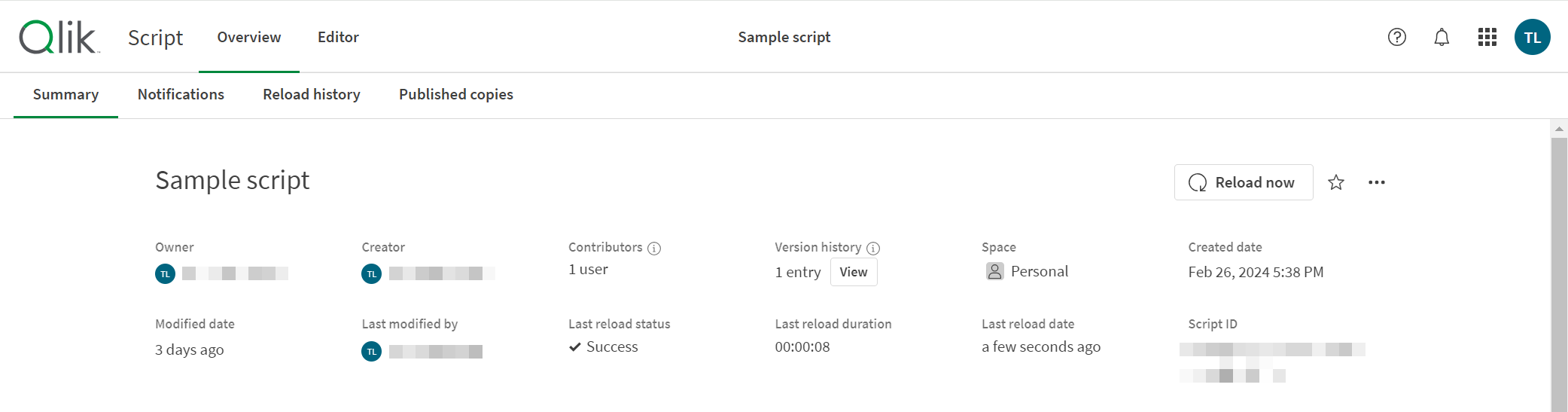
You can view time information in that Updated timestamp that is shown in the script tile. You can also see this information by clicking on a script to open Overview. It is listed in Summary as Modified date. The format of the date may differ; for example, if the script was recently updated, the Updated value on the script tile may appear as follows: Updated 15 minutes ago.
You can view Last reload date by selecting on the script, then selecting Details. This value is only refreshed when the script's data is refreshed. A run also changes the Updated and Modified date timestamp.
Modified date and Last reload date fields in script Details
The following table lists the operations that refresh Updated (same as Modified date) and Last reload date timestamps:
| Operation | Updated, Modified date | Last reload date |
|---|---|---|
| Run (reload) | Yes | Yes |
| Change name | Yes | No |
| Change description | Yes | No |
| Publish script | Yes | No |
| Change owner | Yes | No |
| Change script | Yes | No |
