The Radar chart (Radar chart) displays a two-dimensional chart using radial axes to chart one or more groups of values over multiple variables. Radar charts can be used to visualize and compare performance to a set standard or to a group's performance.
Radar charts requires two dimensions and one measure. The y-axis goes from the center to the perimeter and the x-axis is the perimeter of the chart. Each value represents the distance from the center of the chart, and displays on axes starting from the center. The center of the chart represents the minimum value, and the edge the maximum value.
A radar chart can show multiple series, each separately connected with their values. The data only goes around the chart once. Adding values only increases the chart's granularity.
A selection that is made in a radar chart is confirmed instantly. When applicable, make additional selections one at a time.

Understanding a radar chart
A radar chart consists of evenly spaced segments (axes) arranged radially around a point. There is one segment for each data value of the second dimension. The value of each measure is shown by a node on applicable axis. A line connects the values that belong to the same series creating the chart’s star-like shape.
A radar chart with one axis for each month of the Date.Month dimension.
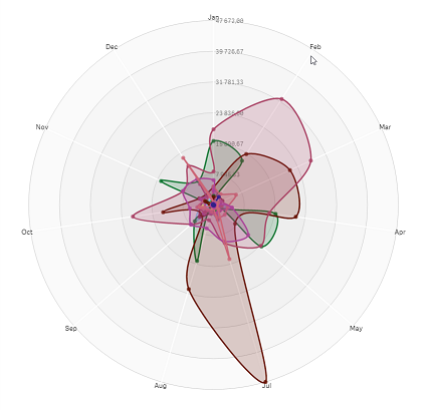
When to use the radar chart
Radar charts let you compare and measure data with an arbitrary number of variables. This is helpful when comparing something's features or performance over several metrics. For example: before buying a computer, you can compare different computers across several features, such as memory storage processing, and screen size. A radar chart is also useful when:
- Measuring quality improvements and performance.
- Comparing allocated amount versus actual spending in an organization.
- Identifying outliers, commonality, and clusters of data with similar values and features.
- Charting an athlete's strengths and weaknesses.
-
Comparing results of small-to-moderate-sized multivariate data sets.
Limitations
Radar charts have the following limitations:
- Radar charts can only process 100 unique values per dimension.
- Exported radar charts will not include the chart legend.
- For information about general limitations, see Limitations.
